Preclinical Molecular Imaging Group
Dr Gabriela Kramer-Marek’s group uses cutting-edge biomedical imaging techniques to gain information about the way particular genes drive cancer progression.
Our group’s long-term goal is to develop specific biomarkers for detecting cancers and to evaluate these biomarkers in pre-clinical cancer models
Notwithstanding the remarkable clinical success of mAb-based treatment regimens, not all patients benefit from them. This can be attributed, at least in part, to the complexity of the tumour microenvironment and its considerable heterogeneity both in terms of the tumour and non-tumour cell components. These phenomena represent a huge challenge in identifying predictive biomarkers and stratifying patient populations for personalised therapy approaches.
Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop assays that will help in three ways:
- accurate patient selection
- understanding intrinsic resistance mechanisms or the emergence of acquired resistance following treatment initiation and
- choosing the most effective combination regimen in circumstances in which single-agent therapies are insufficiently effective.
Currently, the baseline expression level of antigens targeted by therapeutic mAbs can be analysed by methods such as: immunohistochemistry (IHC), flow cytometry, proteomics, or next-generation sequencing of tumour tissues acquired at diagnostic biopsy or intra-operatively. These techniques aid our understanding of how cancer cells adapt to treatment and become resistant, but such methods are inherently invasive, prone to sampling errors caused by inter- and intra-tumour heterogeneity of receptor expression within analysed biopsy specimens and do not lend themselves readily to repeated sampling.
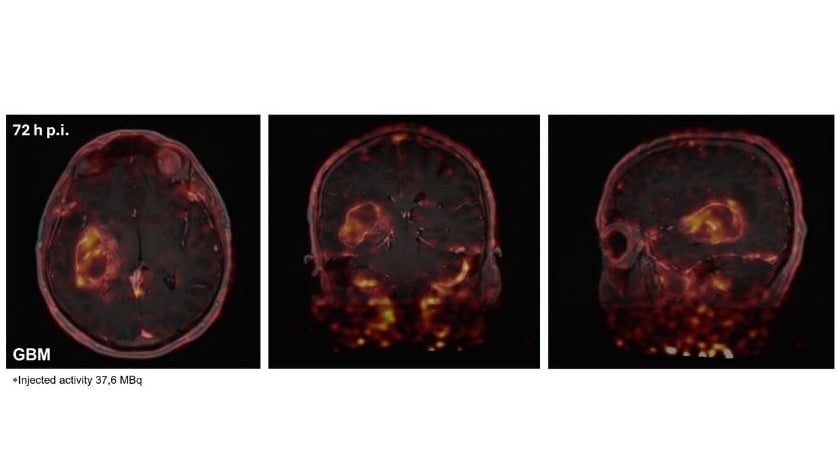
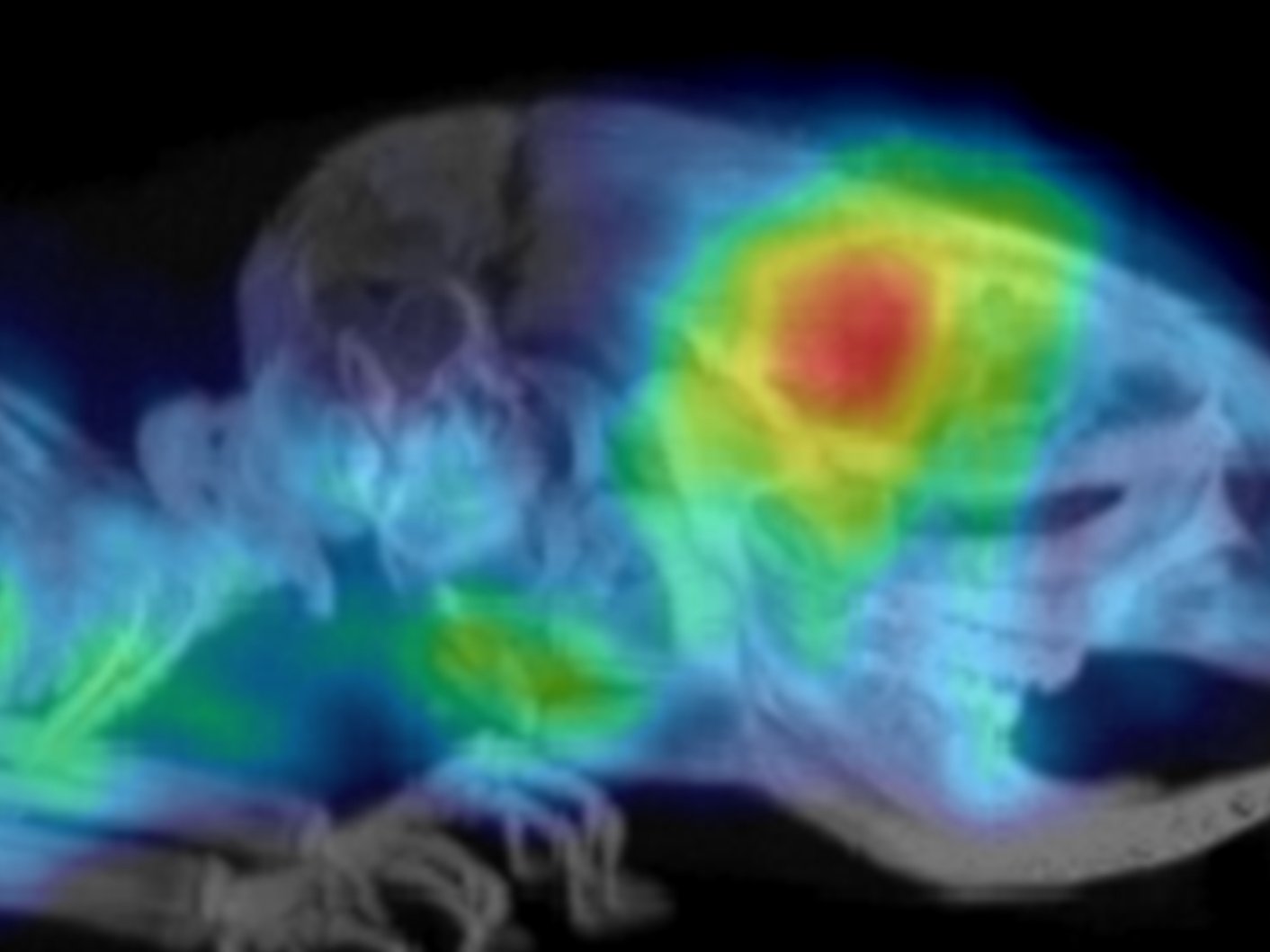
Positron emission tomography (PET), using radiolabelled mAbs, antibody fragments or engineered protein scaffolds (immuno-PET), has the potential to acquire information non-invasively and can be highly complementary to analyses based on tissue acquisition. Accordingly, immuno-PET agents might accurately identify the presence and accessibility of the target and provide a rapid assessment of tumour response to a variety of treatments in a timely fashion (e.g. within 1-2 weeks of treatment initiation).
Furthermore, immuno-PET agents can provide information about the heterogeneity of both target expression and therapeutic response, which are increasingly recognised as key factors in treatment resistance. This especially relates to patients with advanced disease in whom target expression may vary from site to site and a biopsy of a single local or metastatic deposit may not accurately reflect the situation across the entire disease burden. Although introduction of immuno-PET into routine clinical practice may add complexity and increase costs, with appropriate use this imaging modality has the potential to identify patients likely to benefit from therapy and assess the efficacy of novel target-specific drugs.
Against this background, our research focuses on the development and characterisation of targeted-PET radiotracers, including protein-based theranostic agents that enable smart monitoring of immunotherapies and expand opportunities for personalised medicine approaches.
Early diagnosis and individualized therapy have been recognized as crucial for the improvement of cancer treatment outcome. While proper molecular characterization of individual tumour types facilitates choice of the right therapeutic strategies, early assessment of tumour response to therapy could allow the physicians to discontinue ineffective treatment and offer the patient a more promising alternative. Therefore, the role of molecular imaging in elucidating molecular pathways involved in cancer progression and the ability to select the most effective therapy based on the unique biologic characteristics of the patient and the molecular properties of a tumour are undoubtedly of paramount importance.
The mission of this group is to investigate innovative imaging probes and apply them to novel orthotopic or metastatic models that are target driven, to gain information of the way particular oncogenes drive cancer progression through signalling pathways that can be imaged in vivo and, correlate it with target level ex vivo. Such an approach enables non-invasive assessment of biochemical target levels, target modulation and provides opportunities to optimize the drug dosing for maximum therapeutic effect, which leads to the development of better strategies for the more precise delivery of medicine.
The long term goal of our research is to develop specific imaging cancer biomarkers, especially for positron emission tomography (PET) as well as optical imaging and, evaluate these biomarkers in pre-clinical cancer models. Significant efforts are directed towards validating biomarkers for early prediction of treatment response, with the focus on new targeted therapies (such as inhibition of cell signalling pathways).
Our initial portfolio of imaging agents include radiolabelled affibody molecules, TK inhibitors and, conventional tracers that monitor universal markers of tumour physiology.
We are actively supported by other groups from the Division of Radiotherapy and Imaging as well as the Division of Cancer Therapeutics. Moreover, our close association with The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust enables rapid translation of our research to early clinical studies and ensures a fast transition of know-how from the research laboratory to the patient bedside.
Dr Gabriela Kramer-Marek
Group Leader:
Preclinical Molecular Imaging
Dr Gabriela Kramer-Marek is investigating new ways of molecular imaging in order to predict an individual patient’s response to treatment. Before moving to the ICR, she developed a new approach for non-invasive assessment of HER2 expression in breast cancer.
Researchers in this group
Dr Gabriela Kramer-Marek's group have written 63 publications
Most recent new publication 2/2025
See all their publications .
.